祝贺课题组柴玉超博士的论文, “Acetylene Selective Hydrogenation Catalyzed by Cationic Nickel Confined in Zeolite”, 被J Am Chem Soc接收。
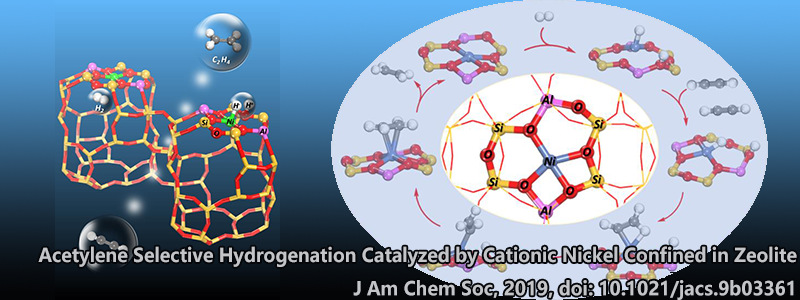
The selective hydrogenation of alkynes to alkenes is an important type of organic transformation with large-scale industrial applications. This transformation requires efficient catalysts with precise selectivity control, and palladium-based metallic catalysts are currently employed. Here we show that four-coordinated cationic nickel (II) confined in zeolite can efficiently catalyze the selective hydrogenation of acetylene to ethylene, a key process for trace acetylene removal prior to polymerization process. Under optimized conditions, 100% acetylene conversion and the ethylene selectivity up to 97% are simultaneously achieved. This catalyst system also exhibits good stability and recyclability for potential application. Spectroscopy investigations and density functional theory calculations reveal the heterolytic dissociation of hydrogen molecule and the importance of hydride and proton in the selective hydrogenation of acetylene to ethylene. This work provides an efficient strategy toward active and selective zeolite catalysts by utilizing the local electrostatic field within zeolite confined space for small molecule activation and by linking heterogeneous and homogenous catalysis.
