祝贺课题组2020届博士孙兰兰关于甲烷选择催化氧化的研究论文,“Water-involved methane-selective catalytic oxidation by dioxygen over copper zeolites”,被Chem发表。
Water-involved methaneselective oxidation by dioxygen over Cu–CHA zeolite catalyst
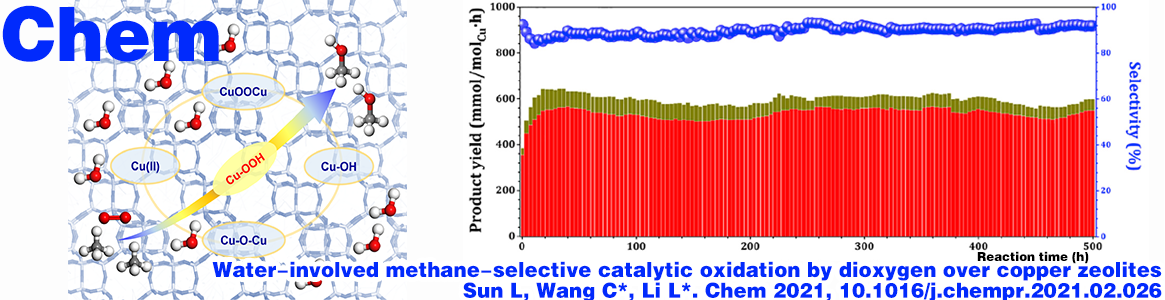
Methanol space-time yield of 543 mmol/molCu/h achieved at methanol selectivity of 91%
Both monomeric and dimeric Cu species can catalyze the methaneto-methanol conversion
Various Cu species undergo interconversion under employed reaction conditions
The selective oxidation of methane to methanol is a dream reaction of direct methane functionalization, which remains a key challenge in catalysis and a hot topic of controversy. Herein, we report the water-involvedmethane-selective catalytic oxidation by dioxygen over copper zeolites. At 573 K, a state-of-the-art methanol space-time yield of 543 mmol/molCu/h with methanol selectivity of 91% is achieved with a Cu–CHA catalyst. Temperature-programmed surface reactions with isotope labeling suggest water as the apparent oxygen and hydrogen source of hydroxyl in methanol. Spectroscopic analyses reveal the fast redox cycle of Cu2+-Cu+-Cu2+ during methane-selective oxidation, which is closely related to the high catalytic activity of Cu–CHA. Density functional theory calculations suggest that both CuOH monomer and dimer in Cu–CHA can catalyze the selective oxidation of methane to methanol with Cu–OOH as the key reaction intermediate, and meanwhile, various copper sites may undergo interconversion under reaction conditions.
